Currently, I’m working on re-building my database and models. In this series I will take you through the process. The aim is to be as transparent and precise as possible. I will share all my code and all my files for everyone to use. Hopefully, this can be helpful in getting more people into hockey and hockey analytics.
I like to think that one of my biggest strengths is my ability to explain complex matters in an easy-to-understand manner. The goal is to write a series which everyone can follow – Even without any pre-coding experience.
Previous articles in the Series:
- Getting data directly from the NHL Api
- Cleaning and Transforming NHL data in MySQL
- Building xG Models in Python
- Testing the xG Models
Expected Goals – The approach in version 2.0
In the first (simple) xG model v. 1.0, we split the data into training (70%) and testing (30%) sets and then built the xG models on the full dataset using logistic regression.
The problem is that the NHL has changed a lot over the years – Goaltender equipment, Shooting for quantity vs. Shooting for quality, Overtime etc.
So, instead of building the xG models over the full dataset we will build running 3-year models – xG_20092010_20112012, xG_20102011_20122013,…, xG_20222023_20242025.
We’re doing 3-year models to have big enough sample sets while not seeing too big changes from the oldest data to the newest data. We will test each model against the following season, so we won’t split the data into testing and training sets.
The final xG model will be the average xG value from each of the relevant 3-year xG models – E.g. a shot from the 20142015 season will take the average xG value from these models: xG_20122013_20142015, xG_20132014_20152016 and xG_20142015_20162017.
That is the general approach. We will build 4 different model types:
- XGBoost
- Logistic Regression
- Random Forrest
- XGBoost (without the rebound variable)
We will do this for all Fenwicks (all unblocked shot attempts) and for all shots on net. The shot-based model will be used for goaltender analysis.
All in all, we will be doing 8 different models.
The variables
Using BoxIDs instead of Shot distance and Shot angle:
For the most part, we will be using the same variables as we did in the previous version. The main difference is that we will use BoxIDs+handedness instead of Shot distance and Shot angle. Basically, we will split the ice into zones and use the BoxID of each zone as a categorical variable.

The assumption is that it doesn’t matter whether the shot comes from the left side or the right side, so the BoxIDs are identical on either side.
However, we did see in the previous article that handedness matters when it comes to angled shots. A left-handed shot has a higher goal probability from the right side than the left side. For right-handed shots it’s the opposite. This means that all angled BoxIDs will be labelled as either weak or strong depending on the handedness of the shooter.
Strength States:
We will use Strength State as a variable, and we will use these Strength States: 5v5, PP1 (5v4 or ENF – Empty net for), PP2 (5v3 or 4v3), SH (4v5, 3v5 or 3v4), 4v4 and 3v3.
For seasons prior to the 20152016 season, we’re combining 4v4 and 3v3 to one strength state. Prior to this season the NHL used 4v4 for overtime, so 3v3 hockey was very rare.
Score States:
The score states used are: less than -2, -2, -1, +0, +1, +2 and more than +2.
Shot Types:
The shot types used are: Wrist, snap, slap, backhand, deflection, wrap-around, tip-in and other (e.g. cradle, between-the-legs, poke, bat).
Venue:
Is the game at home or away?
RinkVenues (Rink bias):
The home team + the season (e.g. BOS_20122013, CAR_20242025). When testing the data, we don’t actually have the RinkVenue, because it’s season dependent. Instead, we will create a weighted RinkVenue that puts most weight on the prior season (1/2), a little less on the season 2 years prior (1/3) and the least weight on the season 3 years prior (1/6). This way we’re trying to estimate what the rink bias will be in the testing season.
Last Event (Rebound):
The final variable in these models is Last Event. Here we will have 3 different values: None, Quick and Rebound. If no event happened within 3 seconds of the shot, then the value is None. If a shot attempt, takeaway or giveaway happened within 3 seconds of the shot, then the value is Rebound. If any other event (e.g. hit, faceoff) happened within 3 seconds, then the value is Quick.
In the fourth model type we’re excluding this variable.
Building the xG models
Here’s the Python code used to build the models:
First the data is loaded into a Pandas dataframe. I’m reading the data directly from a MySQL database. In this case I’m loading the fenwick data for the fenwick models:
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
from sqlalchemy.exc import SQLAlchemyError
from sqlalchemy import text
import requests as req
import pandas as pd
username = 'root'
password = '' # MySQL password
host = 'localhost' # or your remote host
port = '3306' # default MySQL port
database = 'public'
# Create the engine
engine = create_engine(f'mysql+mysqlconnector://{username}:{password}@{host}:{port}/{database}')
query = text('SELECT * FROM model_fenwick')
# Execute the query and load into a DataFrame
df = pd.read_sql(query, con=engine)
Then we can build the 3-year models using XGBoost (The models are saved to your computer as .pkl files):
import numpy as np
from xgboost import XGBClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score, log_loss
import joblib
# Define features and target
feature_cols = ["Venue", "shotType2", "ScoreState2", "RinkVenue", "StrengthState2", "BoxID2", "LastEvent"]
target_col = "Goal"
# Fill missing values and convert to string
df[feature_cols] = df[feature_cols].fillna("missing").astype(str)
df["Season"] = df["Season"].astype(str).str.strip()
# Sort seasons
seasons = sorted(df["Season"].unique())
window_size = 3
models = {}
results = []
# Replace RinkVenue in test seasons with synthetic weighted labels
def build_weighted_rinkvenue_map(df, train_seasons):
weights = [1/6, 1/3, 1/2]
rink_map = {}
for season, weight in zip(train_seasons, weights):
season_df = df[df["Season"] == season]
for rink in season_df["RinkVenue"].unique():
if "-" not in rink:
continue
team = rink.split("-")[1]
rink_map.setdefault(team, []).append((season, weight))
return rink_map
for i in range(len(seasons) - window_size + 1):
train_seasons = seasons[i:i+window_size]
test_season_index = i + window_size
test_season = seasons[test_season_index] if test_season_index < len(seasons) else None
model_name = f"{train_seasons[0]}_{train_seasons[-1]}"
# Replace RinkVenue values in test season
if test_season:
rink_map = build_weighted_rinkvenue_map(df, train_seasons)
test_idx = df["Season"] == test_season
for idx in df[test_idx].index:
original_rink = df.at[idx, "RinkVenue"]
if "-" in original_rink:
team = original_rink.split("-")[1]
df.at[idx, "RinkVenue"] = f"weighted_{team}"
# Create dummy variables
X_full = pd.get_dummies(df[feature_cols]).astype(float)
y_full = df[target_col]
# Main loop
for i in range(len(seasons) - window_size + 1):
train_seasons = seasons[i:i+window_size]
test_season_index = i + window_size
test_season = seasons[test_season_index] if test_season_index < len(seasons) else None
model_name = f"{train_seasons[0]}_{train_seasons[-1]}"
# Split training data
train_idx = df["Season"].isin(train_seasons)
X_train = X_full[train_idx].copy()
y_train = y_full[train_idx]
X_train = X_train.astype(float)
# Train model
model = XGBClassifier(eval_metric="logloss")
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
models[model_name] = model
joblib.dump(model, f"xgb_{model_name}.pkl")
# Predict for training seasons
for season in train_seasons:
season_idx = df["Season"] == season
X_season = X_full[season_idx].copy()
missing_cols = set(X_train.columns) - set(X_season.columns)
for col in missing_cols:
X_season[col] = 0
extra_cols = set(X_season.columns) - set(X_train.columns)
X_season.drop(columns=extra_cols, inplace=True)
X_season = X_season[X_train.columns].astype(float)
df.loc[season_idx, f"xG_{model_name}"] = model.predict_proba(X_season)[:, 1]
# Predict for test season if available
if test_season:
test_idx = df["Season"] == test_season
X_test = X_full[test_idx].copy()
# Reconstruct weighted RinkVenue values
for idx in X_test.index:
rink_label = df.at[idx, "RinkVenue"]
if rink_label.startswith("weighted_"):
team = rink_label.split("_")[1]
for season, weight in zip(train_seasons, [1/6, 1/3, 1/2]):
col_name = f"RinkVenue_{season}-{team}"
if col_name in X_test.columns:
X_test.at[idx, col_name] = weight
# Drop synthetic RinkVenue columns
drop_cols = [col for col in X_test.columns if col.startswith("RinkVenue_weighted_")]
X_test.drop(columns=drop_cols, inplace=True, errors='ignore')
# Align columns
missing_cols = set(X_train.columns) - set(X_test.columns)
for col in missing_cols:
X_test[col] = 0
extra_cols = set(X_test.columns) - set(X_train.columns)
X_test.drop(columns=extra_cols, inplace=True)
X_test = X_test[X_train.columns].astype(float)
# Predict and evaluate
df.loc[test_idx, f"xG_test_{model_name}"] = model.predict_proba(X_test)[:, 1]
y_pred = df.loc[test_idx, f"xG_test_{model_name}"]
y_true = y_full[test_idx]
mask = (~y_pred.isna()) & (~y_true.isna())
y_pred_clean = y_pred[mask]
y_true_clean = y_true[mask]
if len(y_true_clean) > 0:
auc = roc_auc_score(y_true_clean, y_pred_clean)
logloss = log_loss(y_true_clean, y_pred_clean)
results.append({
"Model": model_name,
"TestSeason": test_season,
"AUC": round(auc, 4),
"LogLoss": round(logloss, 4),
"Samples": len(y_true_clean)
})
else:
print(f"Skipping {model_name} → {test_season}: no valid samples.")
else:
print(f"{model_name}: no test season available, model trained for future use.")
# Final xG average
xg_cols = [col for col in df.columns if col.startswith("xG_")]
df["xG_avg"] = df[xg_cols].mean(axis=1)
# Summary table
results_df = pd.DataFrame(results)
print(results_df)
Finally, the data can be written back to the MySQL database:
df.to_sql(
name='nhl_xg_f_data1',
con=engine,
if_exists='replace',
index=False,
chunksize=10000 # Adjust chunk size based on your memory
)
This process is then repeated. You re-load the Fenwick data from MySQL, and then you can build the Logistic Regression models:
import numpy as np
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score, log_loss
import joblib
# Define features and target
feature_cols = ["Venue", "shotType2", "ScoreState2", "RinkVenue", "StrengthState2", "BoxID2", "LastEvent"]
target_col = "Goal"
# Fill missing values and convert to string
df[feature_cols] = df[feature_cols].fillna("missing").astype(str)
df["Season"] = df["Season"].astype(str).str.strip()
# Sort seasons
seasons = sorted(df["Season"].unique())
window_size = 3
models = {}
results = []
# Replace RinkVenue in test seasons with synthetic weighted labels
def build_weighted_rinkvenue_map(df, train_seasons):
weights = [1/6, 1/3, 1/2]
rink_map = {}
for season, weight in zip(train_seasons, weights):
season_df = df[df["Season"] == season]
for rink in season_df["RinkVenue"].unique():
if "-" not in rink:
continue
team = rink.split("-")[1]
rink_map.setdefault(team, []).append((season, weight))
return rink_map
for i in range(len(seasons) - window_size + 1):
train_seasons = seasons[i:i+window_size]
test_season_index = i + window_size
test_season = seasons[test_season_index] if test_season_index < len(seasons) else None
model_name = f"{train_seasons[0]}_{train_seasons[-1]}"
# Replace RinkVenue values in test season
if test_season:
rink_map = build_weighted_rinkvenue_map(df, train_seasons)
test_idx = df["Season"] == test_season
for idx in df[test_idx].index:
original_rink = df.at[idx, "RinkVenue"]
if "-" in original_rink:
team = original_rink.split("-")[1]
df.at[idx, "RinkVenue"] = f"weighted_{team}"
# Create dummy variables
X_full = pd.get_dummies(df[feature_cols]).astype(float)
y_full = df[target_col]
# Main loop
for i in range(len(seasons) - window_size + 1):
train_seasons = seasons[i:i+window_size]
test_season_index = i + window_size
test_season = seasons[test_season_index] if test_season_index < len(seasons) else None
model_name = f"{train_seasons[0]}_{train_seasons[-1]}"
# Split training data
train_idx = df["Season"].isin(train_seasons)
X_train = X_full[train_idx].copy()
y_train = y_full[train_idx]
X_train = X_train.astype(float)
# Train logistic regression model
model = LogisticRegression(solver="liblinear", max_iter=1000)
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
models[model_name] = model
joblib.dump(model, f"logreg_{model_name}.pkl")
# Predict for training seasons
for season in train_seasons:
season_idx = df["Season"] == season
X_season = X_full[season_idx].copy()
missing_cols = set(X_train.columns) - set(X_season.columns)
for col in missing_cols:
X_season[col] = 0
extra_cols = set(X_season.columns) - set(X_train.columns)
X_season.drop(columns=extra_cols, inplace=True)
X_season = X_season[X_train.columns].astype(float)
df.loc[season_idx, f"xG_logreg_{model_name}"] = model.predict_proba(X_season)[:, 1]
# Predict for test season if available
if test_season:
test_idx = df["Season"] == test_season
X_test = X_full[test_idx].copy()
# Reconstruct weighted RinkVenue values
for idx in X_test.index:
rink_label = df.at[idx, "RinkVenue"]
if rink_label.startswith("weighted_"):
team = rink_label.split("_")[1]
for season, weight in zip(train_seasons, [1/6, 1/3, 1/2]):
col_name = f"RinkVenue_{season}-{team}"
if col_name in X_test.columns:
X_test.at[idx, col_name] = weight
# Drop synthetic RinkVenue columns
drop_cols = [col for col in X_test.columns if col.startswith("RinkVenue_weighted_")]
X_test.drop(columns=drop_cols, inplace=True, errors='ignore')
# Align columns
missing_cols = set(X_train.columns) - set(X_test.columns)
for col in missing_cols:
X_test[col] = 0
extra_cols = set(X_test.columns) - set(X_train.columns)
X_test.drop(columns=extra_cols, inplace=True)
X_test = X_test[X_train.columns].astype(float)
# Predict and evaluate
df.loc[test_idx, f"xG_logreg_test_{model_name}"] = model.predict_proba(X_test)[:, 1]
y_pred = df.loc[test_idx, f"xG_logreg_test_{model_name}"]
y_true = y_full[test_idx]
mask = (~y_pred.isna()) & (~y_true.isna())
y_pred_clean = y_pred[mask]
y_true_clean = y_true[mask]
if len(y_true_clean) > 0:
auc = roc_auc_score(y_true_clean, y_pred_clean)
logloss = log_loss(y_true_clean, y_pred_clean)
results.append({
"Model": model_name,
"TestSeason": test_season,
"AUC": round(auc, 4),
"LogLoss": round(logloss, 4),
"Samples": len(y_true_clean)
})
else:
print(f"Skipping {model_name} → {test_season}: no valid samples.")
else:
print(f"{model_name}: no test season available, model trained for future use.")
# Final xG average
xg_cols = [col for col in df.columns if col.startswith("xG_logreg_")]
df["xG_logreg_avg"] = df[xg_cols].mean(axis=1)
# Summary table
results_df = pd.DataFrame(results)
print(results_df)
Then you do the same, but for the Random Forrest models:
import numpy as np
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score, log_loss
import joblib
# Define features and target
feature_cols = ["Venue", "shotType2", "ScoreState2", "RinkVenue", "StrengthState2", "BoxID2", "LastEvent"]
target_col = "Goal"
# Fill missing values and convert to string
df[feature_cols] = df[feature_cols].fillna("missing").astype(str)
df["Season"] = df["Season"].astype(str).str.strip()
# Sort seasons
seasons = sorted(df["Season"].unique())
window_size = 3
models = {}
results = []
# Replace RinkVenue in test seasons with synthetic weighted labels
def build_weighted_rinkvenue_map(df, train_seasons):
weights = [1/6, 1/3, 1/2]
rink_map = {}
for season, weight in zip(train_seasons, weights):
season_df = df[df["Season"] == season]
for rink in season_df["RinkVenue"].unique():
if "-" not in rink:
continue
team = rink.split("-")[1]
rink_map.setdefault(team, []).append((season, weight))
return rink_map
for i in range(len(seasons) - window_size + 1):
train_seasons = seasons[i:i+window_size]
test_season_index = i + window_size
test_season = seasons[test_season_index] if test_season_index < len(seasons) else None
model_name = f"{train_seasons[0]}_{train_seasons[-1]}"
# Replace RinkVenue values in test season
if test_season:
rink_map = build_weighted_rinkvenue_map(df, train_seasons)
test_idx = df["Season"] == test_season
for idx in df[test_idx].index:
original_rink = df.at[idx, "RinkVenue"]
if "-" in original_rink:
team = original_rink.split("-")[1]
df.at[idx, "RinkVenue"] = f"weighted_{team}"
# Create dummy variables
X_full = pd.get_dummies(df[feature_cols]).astype(float)
y_full = df[target_col]
# Main loop
for i in range(len(seasons) - window_size + 1):
train_seasons = seasons[i:i+window_size]
test_season_index = i + window_size
test_season = seasons[test_season_index] if test_season_index < len(seasons) else None
model_name = f"{train_seasons[0]}_{train_seasons[-1]}"
# Split training data
train_idx = df["Season"].isin(train_seasons)
X_train = X_full[train_idx].copy()
y_train = y_full[train_idx]
X_train = X_train.astype(float)
# Train Random Forest
model = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100, max_depth=5, random_state=42)
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
models[model_name] = model
joblib.dump(model, f"rf_{model_name}.pkl")
# Predict for training seasons
for season in train_seasons:
season_idx = df["Season"] == season
X_season = X_full[season_idx].copy()
missing_cols = set(X_train.columns) - set(X_season.columns)
for col in missing_cols:
X_season[col] = 0
extra_cols = set(X_season.columns) - set(X_train.columns)
X_season.drop(columns=extra_cols, inplace=True)
X_season = X_season[X_train.columns].astype(float)
df.loc[season_idx, f"xG_rf_{model_name}"] = model.predict_proba(X_season)[:, 1]
# Predict for test season if available
if test_season:
test_idx = df["Season"] == test_season
X_test = X_full[test_idx].copy()
# Reconstruct weighted RinkVenue values
for idx in X_test.index:
rink_label = df.at[idx, "RinkVenue"]
if rink_label.startswith("weighted_"):
team = rink_label.split("_")[1]
for season, weight in zip(train_seasons, [1/6, 1/3, 1/2]):
col_name = f"RinkVenue_{season}-{team}"
if col_name in X_test.columns:
X_test.at[idx, col_name] = weight
# Drop synthetic RinkVenue columns
drop_cols = [col for col in X_test.columns if col.startswith("RinkVenue_weighted_")]
X_test.drop(columns=drop_cols, inplace=True, errors='ignore')
# Align columns
missing_cols = set(X_train.columns) - set(X_test.columns)
for col in missing_cols:
X_test[col] = 0
extra_cols = set(X_test.columns) - set(X_train.columns)
X_test.drop(columns=extra_cols, inplace=True)
X_test = X_test[X_train.columns].astype(float)
# Predict and evaluate
df.loc[test_idx, f"xG_rf_test_{model_name}"] = model.predict_proba(X_test)[:, 1]
y_pred = df.loc[test_idx, f"xG_rf_test_{model_name}"]
y_true = y_full[test_idx]
mask = (~y_pred.isna()) & (~y_true.isna())
y_pred_clean = y_pred[mask]
y_true_clean = y_true[mask]
if len(y_true_clean) > 0:
auc = roc_auc_score(y_true_clean, y_pred_clean)
logloss = log_loss(y_true_clean, y_pred_clean)
results.append({
"Model": model_name,
"TestSeason": test_season,
"AUC": round(auc, 4),
"LogLoss": round(logloss, 4),
"Samples": len(y_true_clean)
})
else:
print(f"Skipping {model_name} → {test_season}: no valid samples.")
else:
print(f"{model_name}: no test season available, model trained for future use.")
# Final xG average
xg_cols = [col for col in df.columns if col.startswith("xG_rf_")]
df["xG_rf_avg"] = df[xg_cols].mean(axis=1)
# Summary table
results_df = pd.DataFrame(results)
print(results_df)
Finally, we can do the same thing for the XGBoost model without the Last_Event variable:
import numpy as np
from xgboost import XGBClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score, log_loss
import joblib
# Define features and target
feature_cols = ["Venue", "shotType2", "ScoreState2", "RinkVenue", "StrengthState2", "BoxID2"]
target_col = "Goal"
# Fill missing values and convert to string
df[feature_cols] = df[feature_cols].fillna("missing").astype(str)
df["Season"] = df["Season"].astype(str).str.strip()
# Sort seasons
seasons = sorted(df["Season"].unique())
window_size = 3
models = {}
results = []
# Replace RinkVenue in test seasons with synthetic weighted labels
def build_weighted_rinkvenue_map(df, train_seasons):
weights = [1/6, 1/3, 1/2]
rink_map = {}
for season, weight in zip(train_seasons, weights):
season_df = df[df["Season"] == season]
for rink in season_df["RinkVenue"].unique():
if "-" not in rink:
continue
team = rink.split("-")[1]
rink_map.setdefault(team, []).append((season, weight))
return rink_map
for i in range(len(seasons) - window_size + 1):
train_seasons = seasons[i:i+window_size]
test_season_index = i + window_size
test_season = seasons[test_season_index] if test_season_index < len(seasons) else None
model_name = f"{train_seasons[0]}_{train_seasons[-1]}"
# Replace RinkVenue values in test season
if test_season:
rink_map = build_weighted_rinkvenue_map(df, train_seasons)
test_idx = df["Season"] == test_season
for idx in df[test_idx].index:
original_rink = df.at[idx, "RinkVenue"]
if "-" in original_rink:
team = original_rink.split("-")[1]
df.at[idx, "RinkVenue"] = f"weighted_{team}"
# Create dummy variables
X_full = pd.get_dummies(df[feature_cols]).astype(float)
y_full = df[target_col]
# Main loop
for i in range(len(seasons) - window_size + 1):
train_seasons = seasons[i:i+window_size]
test_season_index = i + window_size
test_season = seasons[test_season_index] if test_season_index < len(seasons) else None
model_name = f"{train_seasons[0]}_{train_seasons[-1]}"
# Split training data
train_idx = df["Season"].isin(train_seasons)
X_train = X_full[train_idx].copy()
y_train = y_full[train_idx]
X_train = X_train.astype(float)
# Train model
model = XGBClassifier(eval_metric="logloss")
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
models[model_name] = model
joblib.dump(model, f"xgb_{model_name}.pkl")
# Predict for training seasons
for season in train_seasons:
season_idx = df["Season"] == season
X_season = X_full[season_idx].copy()
missing_cols = set(X_train.columns) - set(X_season.columns)
for col in missing_cols:
X_season[col] = 0
extra_cols = set(X_season.columns) - set(X_train.columns)
X_season.drop(columns=extra_cols, inplace=True)
X_season = X_season[X_train.columns].astype(float)
df.loc[season_idx, f"xG_{model_name}"] = model.predict_proba(X_season)[:, 1]
# Predict for test season if available
if test_season:
test_idx = df["Season"] == test_season
X_test = X_full[test_idx].copy()
# Reconstruct weighted RinkVenue values
for idx in X_test.index:
rink_label = df.at[idx, "RinkVenue"]
if rink_label.startswith("weighted_"):
team = rink_label.split("_")[1]
for season, weight in zip(train_seasons, [1/6, 1/3, 1/2]):
col_name = f"RinkVenue_{season}-{team}"
if col_name in X_test.columns:
X_test.at[idx, col_name] = weight
# Drop synthetic RinkVenue columns
drop_cols = [col for col in X_test.columns if col.startswith("RinkVenue_weighted_")]
X_test.drop(columns=drop_cols, inplace=True, errors='ignore')
# Align columns
missing_cols = set(X_train.columns) - set(X_test.columns)
for col in missing_cols:
X_test[col] = 0
extra_cols = set(X_test.columns) - set(X_train.columns)
X_test.drop(columns=extra_cols, inplace=True)
X_test = X_test[X_train.columns].astype(float)
# Predict and evaluate
df.loc[test_idx, f"xG_test_{model_name}"] = model.predict_proba(X_test)[:, 1]
y_pred = df.loc[test_idx, f"xG_test_{model_name}"]
y_true = y_full[test_idx]
mask = (~y_pred.isna()) & (~y_true.isna())
y_pred_clean = y_pred[mask]
y_true_clean = y_true[mask]
if len(y_true_clean) > 0:
auc = roc_auc_score(y_true_clean, y_pred_clean)
logloss = log_loss(y_true_clean, y_pred_clean)
results.append({
"Model": model_name,
"TestSeason": test_season,
"AUC": round(auc, 4),
"LogLoss": round(logloss, 4),
"Samples": len(y_true_clean)
})
else:
print(f"Skipping {model_name} → {test_season}: no valid samples.")
else:
print(f"{model_name}: no test season available, model trained for future use.")
# Final xG average
xg_cols = [col for col in df.columns if col.startswith("xG_")]
df["xG_avg"] = df[xg_cols].mean(axis=1)
# Summary table
results_df = pd.DataFrame(results)
print(results_df)
Now the exact same code can be executed again, but this time we just load the shot data instead of our fenwick data. All in all, we will end up with 8 models: 4 fenwick-based models and 4 shot-based models.
Descriptive model testing
We will use AUC and Logloss to test the different models. It’s important to know that for all models that start with xG_Model we’re running the tests on training data. All the models that start with xG_Test are based on testing data, which in our case is the following season. This means that all our testing results are based on old data.
Had we split the data into a training set and a testing set, then we would have had better results on the testing data because it wouldn’t be based on old models.
AUC and Log loss at 5v5:

Obviously, we see the training data perform better than the testing data based on old models. The XGBoost model performs better than the logistic regression model – Both on the training data and the testing data.
Then random forest model is pretty bad, so there’s probably something that’s not ideal in the Python code.
The shot-based model and the fenwick-based model show the exact same trends, but of course the fenwick-based model performs better in terms of logloss.
AUC and Log loss at All Strengths:
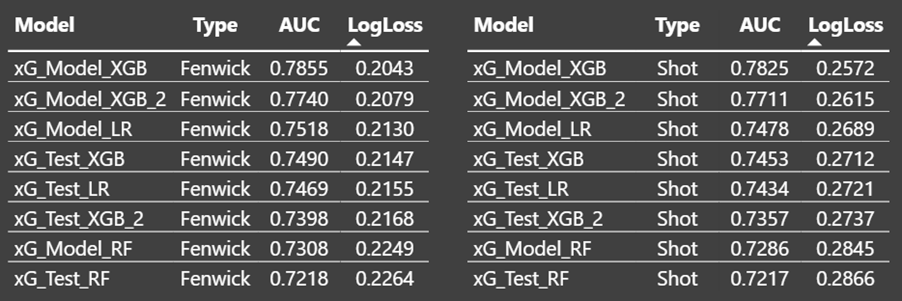
The model rankings at all strengths are exactly the same as they were at 5v5.
GSAx (eye test):
Lastly, we will look at GSAx. This is more of an eye test. Here are the best goaltenders since the 2009/2010 season (only regular season data). I’ve ranked the goalies by the shot-based model, because I don’t believe goaltenders have any meaningful impact on shot misses.

You can always discuss one way or the other with these kinds of lists, but there is nothing here that concerns me model-wise. It looks like a pretty decent list to me.
Predictive model testing
Now, we will test how predictive the xG models are of future results. For this analysis we will only use the testing data.
Test setup:
The idea is to pick x random games for each team and then see how well xGF% for those games can predict GF% for the remainder 82-x games. I’m excluding all non-82-game seasons from this test (2012/2013, 2019/2020 and 2020/2021).
First, I’m picking 10 random games (5 home games and 5 away games) and calculating xGF% (for all the models), GF%, CF%, FF%, SF% for the 10 games as well as the 72 remaining games. I repeated this process 200 times.
Then I do the same thing with 12 games (6 home and 6 away), 14 games, 16 games and all the way up 70 games.
Once I have all the simulation data, we can calculate R^2 for GF% (selected games) vs. GF% (remaining games), xGF% (selected games) vs. GF% (remaining games), and so on. We’re always comparing against GF% (remaining games), because we want to predict future results.
Here are the results for the different xG models:
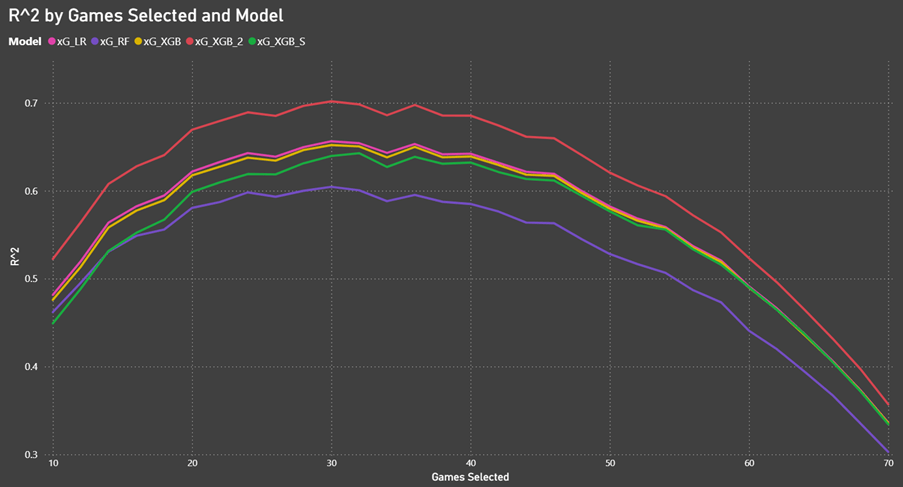
The XGBoost and Logistic regression models show almost the same results, but if we exclude the Last_Event (rebounds) variable, then we see much better results (xG_XGB_2). This is exactly what we expected based on previous research. If the goal is to predict future results, then you shouldn’t give rebound shots a higher xG value.
Here are the results for xG_XGB_2 versus the counting metrics:
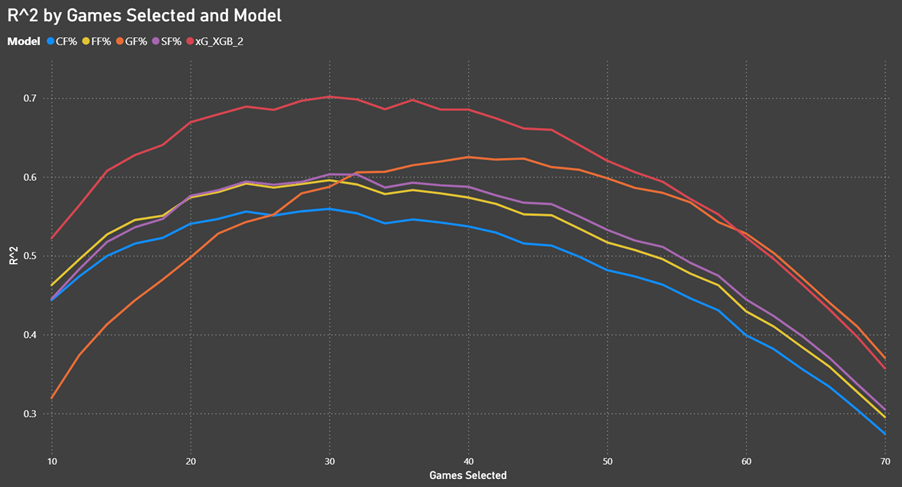
We see that the xG model outperforms SF%, FF% and CF% when it comes to predicting future goals. It’s a little surprising that CF% is performing worse than FF% and SF%.
Variable importance
Importance over time for each of the 3-year models.

We see a few important things here. First of all, we see that BoxID (Shot location + handedness) is by far the most important feature. There’s nothing surprising about this at all.
Secondly, we see that the RinkVenue was most important in the early models. This indicates that the Rink Bias is much less important today than early on. The data tracking has improved over time.
Thirdly, we see the Last_Event feature being more important in the early seasons. I’m not quite sure why this is.
Implementation
Now, we have built and tested the different xG models, so how will we use them? I think it’s important to split the xG into a historic category and a present category.
With the historical data we can build the 3-year models and calculate the average xG values. I think this gives us the best descriptive data. However, we don’t have this luxury with present data, so for the upcoming season we will have to use the latest 3-year model: xG_20222023_20242025.
Once the season is done, we can build a new 3-year model, and we can re-calculate our historic xG data.
I think this is the smartest approach.
Contact
Please reach out if you have comments/questions or if you want to share your own work. I will gladly post it on my platforms.
You can contact me on: hockeystatistics.com@gmail.com